Welcome to part 2 of our 2020 year-end cybersecurity observations. In the first part, we talked about the dominating cybersecurity trends that we observed in KNOW – our threat intel platform and cybersecurity news aggregator. In this part, we are going to see the top 5 ransomware and the top 10 vulnerabilities of 2020.
Top 5 Ransomware of 2020
As observed in KNOW, the top 5 ransomware of 2020 were:
- Maze
- Ryuk
- REvil
- Doppelpaymer
- Egregor
#1 Maze
Maze is an incredibly sophisticated strain of Windows ransomware that has hit companies and organizations around the world. Maze ransomware was first discovered in 2019 and was initially distributed via spam emails and exploit kits before shifting to being deployed post-compromise.
The ransomware’s primary goal is to encrypt all files in an infected system and then demand a ransom to recover the files. It also maintains a public-facing website where they post data stolen from victims who refuse to pay an extortion fee. In April 2020, it hit IT services giant Cognizant, causing service disruptions.
On November 1, 2020, the Maze ransomware gang officially announced that they will be retiring from all activities.
Industries targetted
- Finance
- Healthcare
- Information technology
- Computer hardware
- Consumer electronics
- Insurance
Reference count
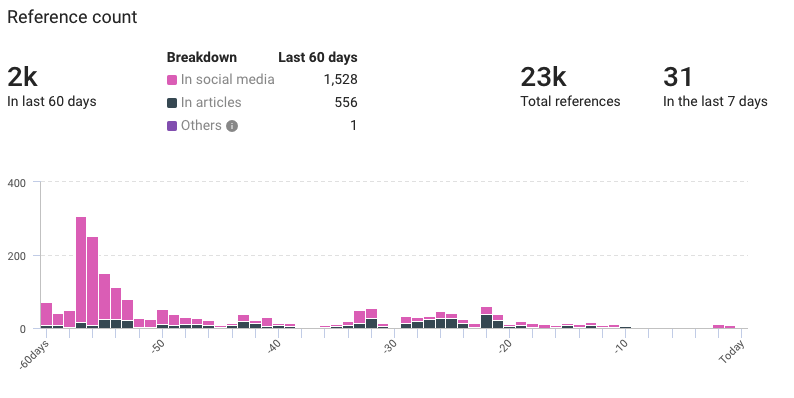
- Total: 23,000
- Previous 60 days: 2,000
- Last 7 days: 31
Maze threat intel context from KNOW
- Risk rules triggered: 7 out of 48
- IPs: 37
- Domains: 107
- Hashes: 160
- URLs: 878
- Vulnerabilities detected: CVE-2018-4878 CVE-2018-8174 CVE-2018-15982 CVE-2019-11510 CVE-2019-19781
- Related Threat Actors: AnonSec APT1 Comment Crew FIN6 Anonymous APT41 TA2101
#2 Ryuk
Ryuk ransomware first appeared in August 2018. While not incredibly active across the globe, at least three organizations were hit with Ryuk infections over the first two months of their operations, landing the attackers about $640,000 in ransom for their efforts.
Ryuk itself possesses functionality that you would see in a few other modern ransomware families. This includes the ability to identify and encrypt network drives and resources and delete shadow copies on the endpoint. By doing this, the attackers could disable the Windows System Restore option for users, making it impossible to recover from the attack without external backups.
The Ryuk ransom note is written to a file named RyukReadMe.txt. The template’s body remains the same, whereas the email ID and the Bitcoin (BTC) wallet address keep changing. It remains unclear if WIZARD SPIDER is copying the TTPs (tactics, techniques, and procedures) and ransom notes of BitPaymer, or whether the groups may share information with each other.
Industries targeted
- Healthcare
- Energy and natural resources
- Hospitals
- Education
- Media and entertainment
- Information technology
References counted from KNOW
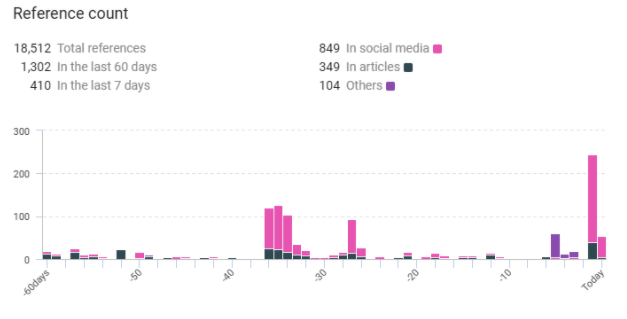
- Total references: 18,512
- Previous 60 days: 1,302
- Last 7 days: 410
Ryuk threat intel context from KNOW
- Recently Linked To Threat Research – 5 sighting(s)
- Hashes: 61
- Vulnerabilities: CVE-2020-1472
- Domains: 1
- Threat actors: Wizard Spider, UNC1878, FIN6, GRIM SPIDER, MixMaster, and Hidden Cobra
- Payload delivered: SystemBC and Buer Loader
- Related intrusion methods: Phishing, Security Breach, Credential Stuffing, Information Stealing, Data Exfiltration, Spam, Credential Stealing, etc.
- Most recent sandbox sighting: Hybrid Analysis result for ‘bf067039ece6e0d4074fa70d49752678cee69233ee380476a96644c268f75839’
#3 REvil
REvil, aka Sodinokibi, was one of the most active ransomware over 2020. It’s a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model that was discovered back in April 2019. Its multiple infection vectors include exploiting known security vulnerabilities and phishing campaigns. REvil first came to prominence around New year’s Eve 2019 when hackers infected the Travelex currency exchange with the ransomware.
REvil encrypts a user’s files and gains administrative access by exploiting the CVE-2019-2725 vulnerability in Oracle WebLogic.
Industries targetted
- Education
- Healthcare
- Telecommunications
- Banking
- Finance
- Food And Beverage
- Hospitals
- Ecommerce
References counted from KNOW
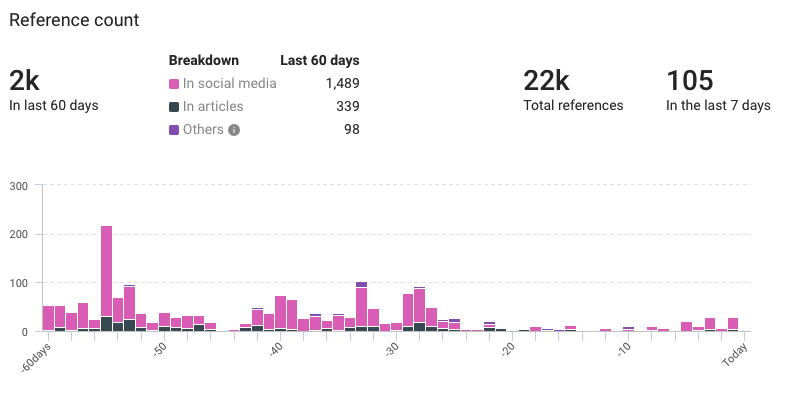
- Total references: 22,000
- Previous 60 days: 2,000
- Last 7 days: 105
REvil threat intel context from KNOW
- Risk rules triggered: 7 out of 48
- Related threat actors: Carbanak and Gold Southfield
- Related intrusion methods: Double Extortion, Phishing, Data Exfiltration, Spam, Phishing Campaign, and 13 more
- Most recent reference: Any Run Sandbox result for d91f951bdcf35012ac6b47c28cf32ec143e4269243d8c229f6cb326fd343df95.exe
- IPs: 3
- Domains: 48
- Hashes: 329
- Vulnerabilities: CVE-2018-8453, CVE-2019-2725, CVE-2019-19781, and CVE-2019-11510.
#4 DoppelPaymer
DoppelPaymer is a ransomware known for attacking enterprise targets. It gains access to systems via admin creds and uses them to compromise the whole system. It has been active since mid-July 2019.
DoppelPaymer is a ransomware family that encrypts user data using RSA-2048 and AES-256 encryption algorithms and later on it asks for a ransom of 100 Bitcoins in order to restore original files.
This ransomware not only locks companies out of their own computer systems by encrypting files but also can exfiltrate company data and use it as collateral. It appends .locked extension to each of the encrypted files, while newer variants mark data with .doppeled appendix.
Industries targeted
- Healthcare
- Telecommunications
- Banking
- Finance
- Food And Beverage
- Hospitals
- Ecommerce
References counted by KNOW
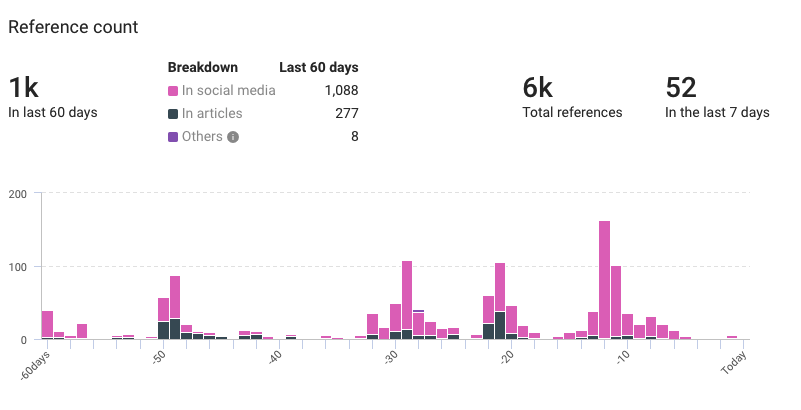
- Total: 6,000
- Previous 60 days: 1,000
- Last 7 days: 52
DoppelPaymer threat intel context from KNOW
- Related intrusion methods: Related Intrusion Methods: Brute Force, Data Exfiltration, Spear Phishing, Data Breach, Security Breach, and 6 more.
- Most recent reference: Hybrid Analysis result for ‘8483aaf9e1fa5b46486c9f2a14c688c30d2006e88de65d0295a57892de0bf4c9.exe’
- Vulnerabilities: CVE-2019-1978 and CVE-2019-19781
- Threat Actors: Evil Corp, TA505, and Indrik Spider.
#5 Egregor
Egregor is a relatively new ransomware that was first spotted in September 2020 and is a variant of Ransom.Sekhmet based on similarities in obfuscation, API-calls, and the ransom note. As per reports, Egregor has already targeted the likes of Barnes & Noble, Kmart, and Ubisoft.
The intrusion method of choice for Egregor is the Cobalt Strike, wherein targeted environments are compromised through methods such as RDP probing and phishing. The Cobalt Strike beacon payload is used to deliver and launch the Egregor payloads.
The overall attack follows two steps:
- Initially, an email lure drops Qakbot, followed by Egregor
- Egregor is used manually by the hackers who managed to gain access via initial compromise.
References counted by KNOW
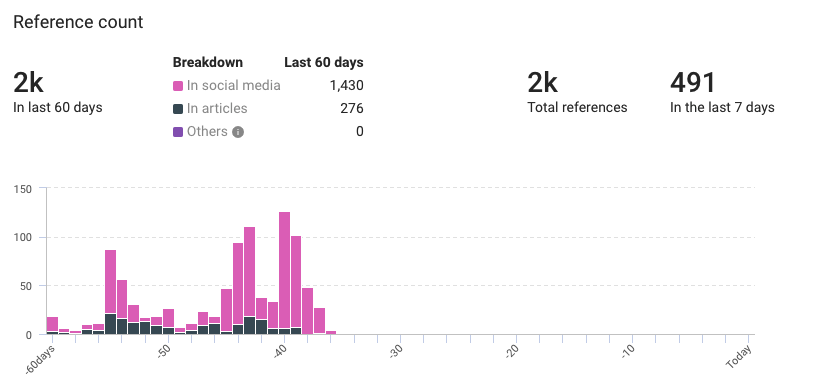
- Total references: 2,000
- Previous 60 days: 2,000
- Last 7 days: 491
Egregor threat intel context from KNOW
- First seen: 14 October 2019
- Related intrusion methods: Obfuscation and Data exfiltrate.
Top 5 ransomware – Ranked by number of hits
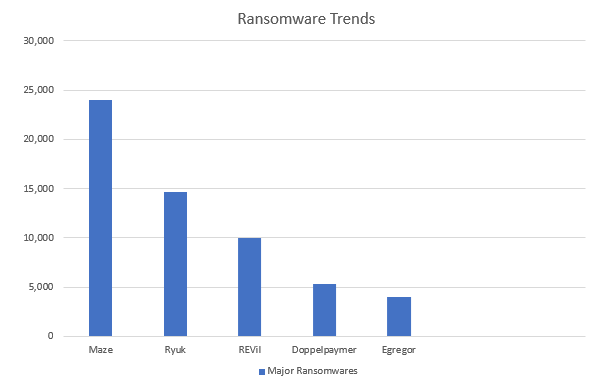
Finally, let’s rank these ransomware groups by the number of hits they generated on KNOW. As you can see, Maze was the most popular ransomware by quite a heavy margin. Ryuk and REvil round off the top 5.
Now that we have seen the top 5 ransomware of 2020, let’s go through the top 10 vulnerabilities of 2020.
Top 10 Vulnerabilities of 2020
As per KNOW, the top 10 vulnerabilities of 2020 are as follows:
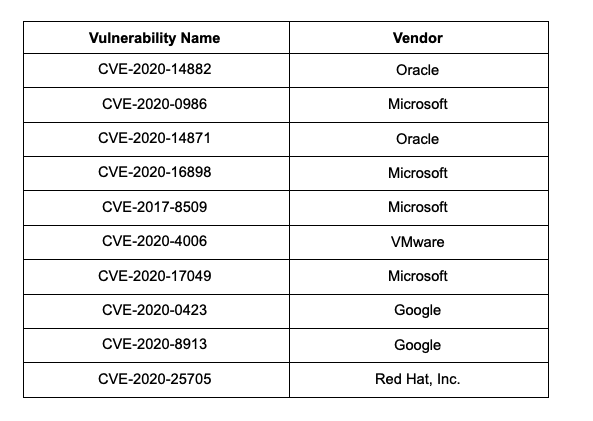
NOTE: We have selected these vulnerabilities based on exploitation and relevance.
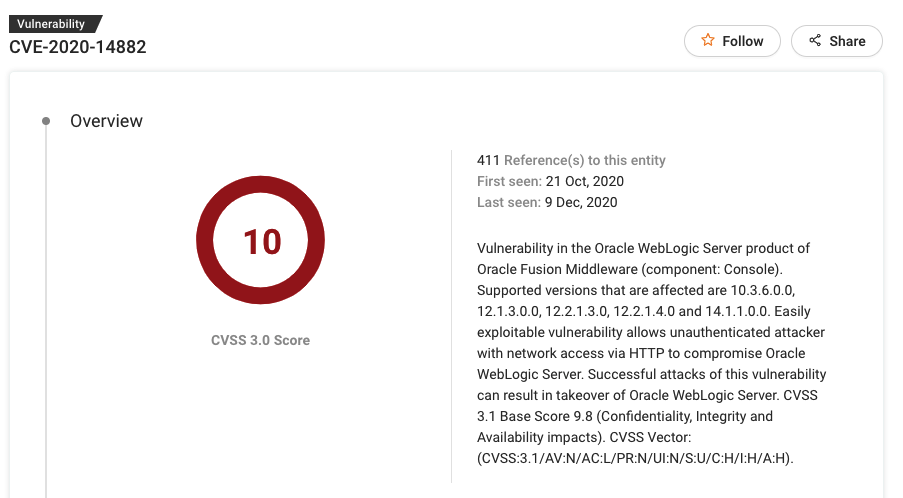
#1 CVE-2020-14882
Patch: https://www.oracle.com/security-alerts/cpuoct2020.html
CVE-2020-14882 is a vulnerability in the Oracle WebLogic Server product of Oracle Fusion Middleware (component: Console).
What happens when you exploit this vulnerability?
It is an easily exploitable vulnerability and allows an unauthenticated attacker with network access via HTTP to completely take over Oracle WebLogic Server. In simple terms, it can be exploited over a network without the need for a username and password.
Supported versions that are affected are 10.3.6.0.0, 12.1.3.0.0, 12.2.1.3.0, 12.2.1.4.0 and 14.1.1.0.0.
#2 CVE-2020-0986
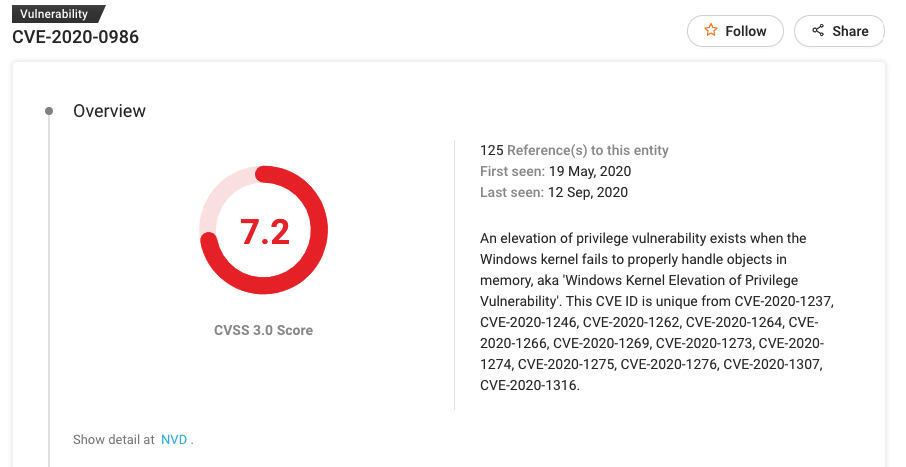
Patch: https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2020-0986
An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly handle objects in memory, aka “Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability.”
What happens when you exploit this vulnerability?
By exploiting CVE-2020-0986, attackers can run arbitrary code in the kernel mode and install programs. Plus, they can view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights.
So, how does an attacker exploit this vulnerability in the first place?
They have to log on to the system and run a specially-crafted application to take control of an affected system.
#3 CVE-2020-14871
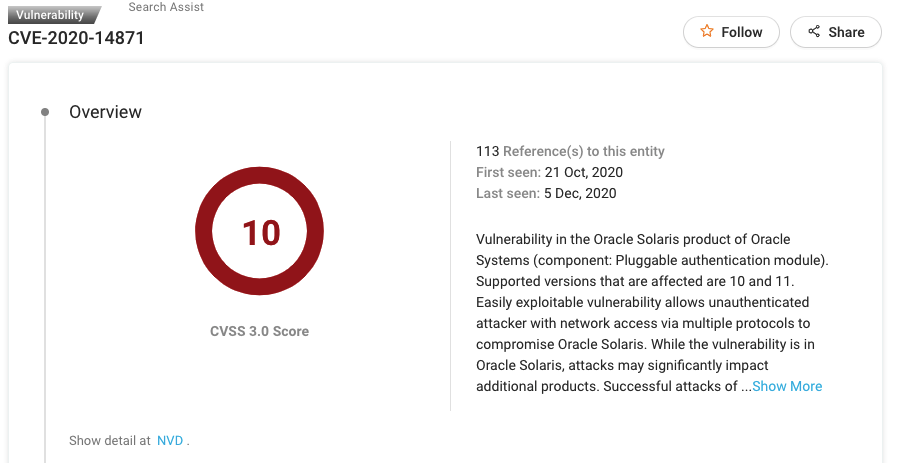
Patch: https://www.oracle.com/security-alerts/cpuoct2020.html
CVE-2020-14871 is a vulnerability in the Oracle Solaris product of Oracle Systems (component: Pluggable authentication module). Supported versions that are affected are 10 and 11.
What happens when you exploit this vulnerability?
What makes it particularly dangerous is that it is very easily exploitable and allows any unauthenticated attacker with network access via multiple protocols to compromise Oracle Solaris. A successful attack can result in a complete Solaris takeover.
Alright, so how does this work?
This vulnerability exists in the PAM library’s parse_user_name function due to the improper input validation of a username that exceeds a certain length (512 bytes).
So, a user can create a specially-crafted request containing a username that exceeds 512 bytes. The attacker could pass limitless input to the PAM parse_user_name function after forcing the keyboard-interactive authentication to prompt for a username.
#4 CVE-2020-16898

Patch: https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2020-1689
CVE-2020-16898 is a remote code execution vulnerability that exists when the Windows TCP/IP stack improperly handles ICMPv6 Router Advertisement packets. This is why it’s also known as Windows TCP/IP Remote Code Execution Vulnerability.
The vulnerability is also called “Bad Neighbor” because it is located within an ICMPv6 Neighbor Discovery “Protocol”, using the Router Advertisement type.
What happens when you exploit this vulnerability?
If a hacker successfully exploits this, they can gain the ability to execute code on the target server or client. The attacker simply sends a specially-crafted ICMPv6 Router Advertisement packet to a remote Windows computer to exploit this vulnerability.
#5 CVE-2020-4006
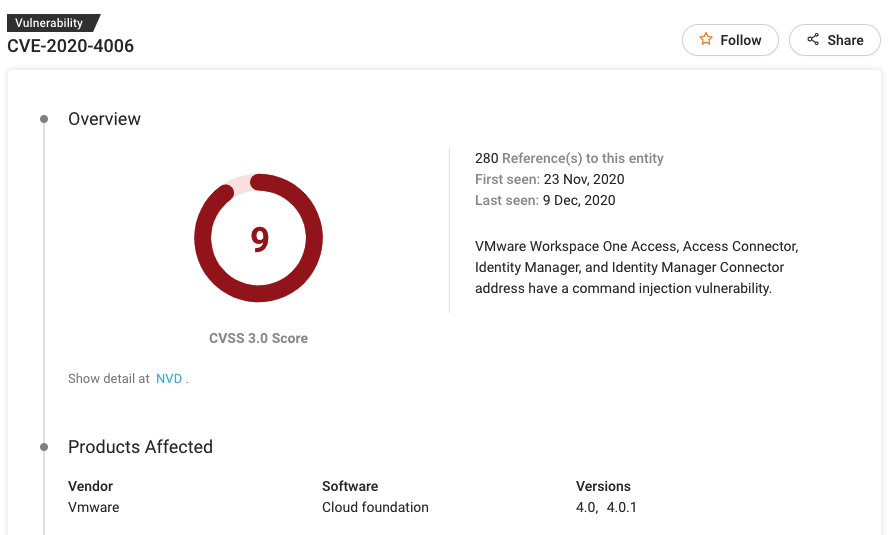
Patch: https://www.vmware.com/security/advisories/VMSA-2020-0027.html
CVE-2020-4006 is a command injection vulnerability in the administrative configurator component in certain versions of VMware products. The list of affected products include:
- VMware Workspace One Access (Access)
- VMware Workspace One Access Connector (Access Connector)
- VMware Identity Manager (vIDM)
- VMware Identity Manager Connector (vIDM Connector)
- VMware Cloud Foundation
- vRealize Suite Lifecycle Manager
What happens when you exploit this vulnerability?
An attacker can exploit the vulnerability by fulfilling two conditions:
- Establishing network access to connect to the administrative configurator, which is typically accessible over port 8443.
- Logging into the configurator with valid administrator credentials.
As per reports from the NSA, Russian state-sponsored threat actors have exploited this vulnerability to install a web shell – a malicious script that can enable remote administration, onto vulnerable systems.
#6 CVE-2017-8509
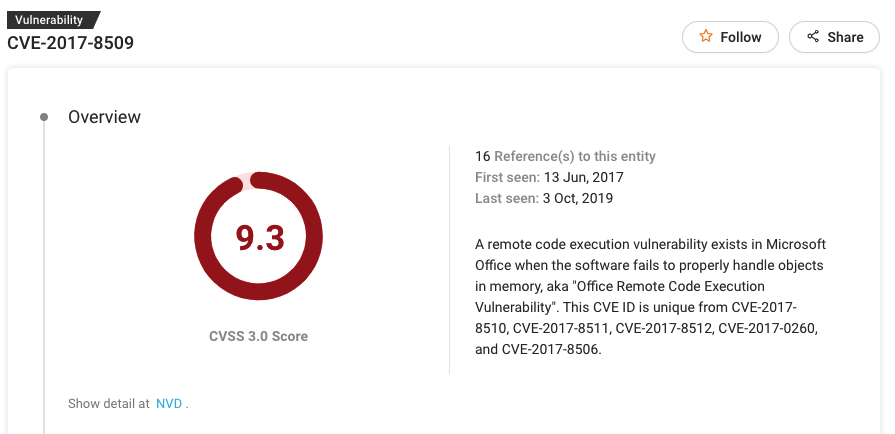
Patch: https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2017-8509
CVE-2017-8509 is a remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Office when the software fails to properly handle objects in memory, aka “Office Remote Code Execution Vulnerability.”
What happens when you exploit this vulnerability?
An attacker can leverage this vulnerability to create a specially crafted file and perform actions in the current user’s security context. If the user opens the file with an affected version of Microsoft Office software, they will kick start the attack. The user gets enticed with a phishing lure to open the file, such as an interesting email or an Instant Messenger message.
#7 CVE-2020-17049
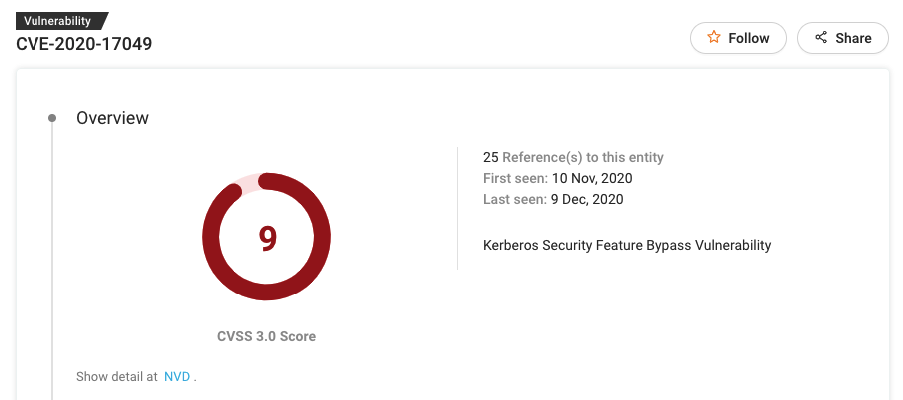
Patch: https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2020-17049
CVE-2020-17049 is a security feature bypass vulnerability that exists in the way Key Distribution Center (KDC) determines if a service ticket can be used for delegation via Kerberos Constrained Delegation (KCD).
This vulnerability is also known as the Kerberos Bronze Bit vulnerability. A compromised service that is configured to use KCD could tamper with a service ticket that is not valid for delegation to force the KDC to accept it.
What happens when you exploit this vulnerability?
Let’s look at two attack scenarios that can be implemented by a hacker:
- They can impersonate users which are not allowed to be delegated. This can include “protected users” or any other users that have been configured as “sensitive and cannot be delegated.”
- The attacker can also launch the attack from a service that has not been allowed to perform the authentication protocol transition.
#8 CVE-2020-0423
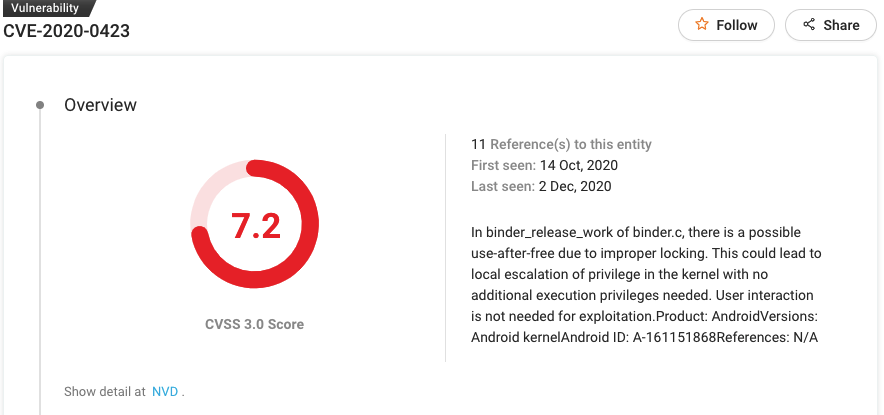
Patch: https://source.android.com/security/bulletin/2020-10-01
In binder_release_work of binder.c, there is a possible use-after-free due to improper locking. This could lead to local escalation of privilege in the kernel with no additional execution privileges needed. As with many vulnerabilities in this list, you don’t require user interaction for exploiting CVE-2020-0423.
#9 CVE-2020-8913
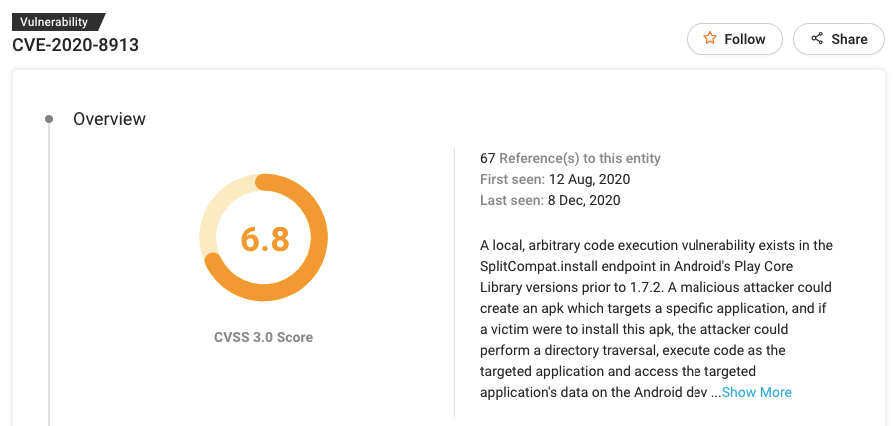
Patch: https://developer.android.com/reference/com/google/android/play/core/release-notes#1-7-2
CVE-2020-8913 is a local, arbitrary code execution vulnerability that exists in the SplitCompat.install endpoint in Android’s Play Core Library versions before 1.7.2.
According to Check Point researchers, of the 13% of Google Play applications analyzed in September 2020, 8% ran a vulnerable variant of the library. This is especially scary because this means that millions of users are potentially at risk of a dangerous cyberattack. Some of the vulnerable apps include OkCupid, MS Edge, Xrecorder, Yango Pro, and PowerDirector.
So, how can an attacker exploit CVE-2020-8913?
A hacker could create an apk that targets a particular application. When the victim installs this apk, the attacker could perform directory traversal and execute code as the targeted application and access the targeted application’s data on the Android device.
#10 CVE-2020-25705
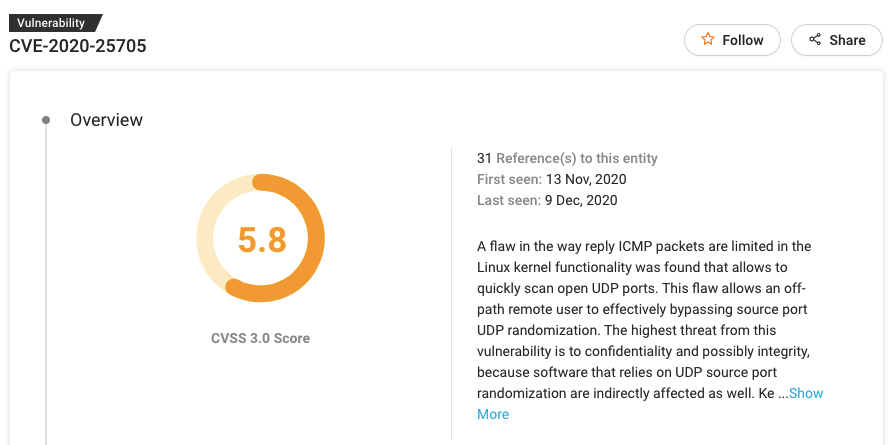
Patch: https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1894579
This is a dangerous flaw in how Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets are limited in the Linux kernel functionality.
How can an attacker exploit CVE-2020-25705?
The CVE-2020-25705 vulnerability enables an off-path remote user to quickly scan open UDP ports and effectively bypass source port UDP randomization. This can significantly affect confidentiality and data integrity. Kernel versions before 5.10 may be vulnerable to this issue.
Why does this flaw exist?
It exists due to rate-limiting controls in the ICMP – an error-reporting protocol that network devices, including routers, use to send error messages to source IP addresses that have introduced an exploitable side channel. This is why this vulnerability is also called “SAD DNS.”
SAD DNS leverages novel network side channels that exist in all modern operating systems, including Linux, Windows, macOS, and FreeBSD.
Top 10 vulnerabilities – Ranking by potency
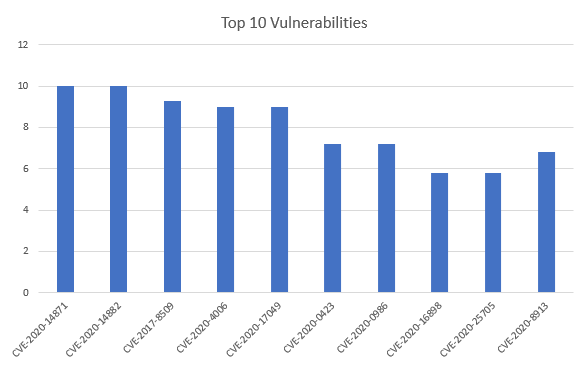
So, we can see the CVE-2020-14871 and CVE-2020-14882 are the two most potent vulnerabilities in the list when we rank by potency. Interesting to note that they are both related to Oracle.
Cybersecurity in 2021: What can change?
2020 has been an absolutely unprecedented year in cybersecurity. However, there is one major lesson that we have learned – proactive security is now more vital than ever before. Threat intelligence should be at the front and center of your SOC’s strategies.
KNOW – Netenrich’s threat intelligence platform – collects intelligence from technical sources and billions of data points across several million online sources and open source threat intelligence (OSINT). You can note the most trending malware, threat actors, attack methods, and vulnerabilities by checking out our threat intel dashboard.
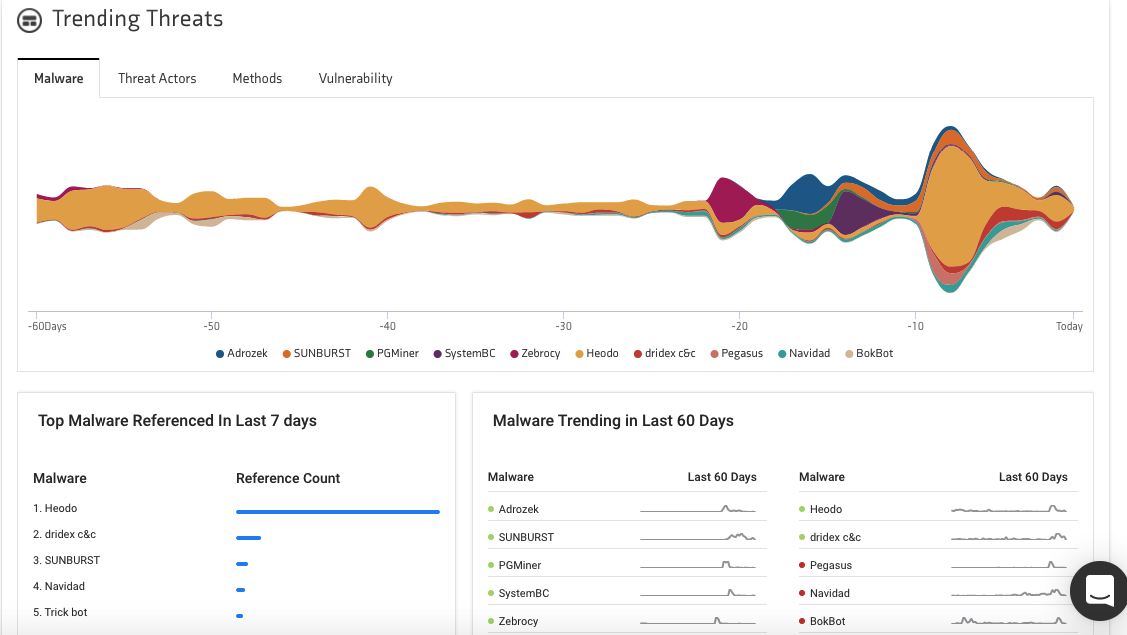
Access critical threat context that covers known associations with IOCs. You can directly copy or export lists to update firewalls, discover domains linked to major threats, uncover new IPs to blacklist, see what industries are being targeted, and much more.
KNOW also aggregates the hottest cybersecurity news and automatically attaches threat context tags and cards to each news article. Always be in the KNOW and stay one step ahead of the bad guys.
The best part of the whole thing is that it is entirely free. You can simply sign up with your email and receive complete access to our threat database, which has 150,000+ entities.
Sign up now and receive a significant boost to your cybersecurity makeup as you head into the new year.
Oh and before we forget.
Threat intelligence is just one side of the coin when comes to our cybersecurity offering. Our true expertise lies in providing comprehensive and holistic security by combining threat and attack surface intelligence. If you are curious and want to find out more then do give this a read.
Subscribe To Our Newsletter!
The best source of information for Security, Networks, Cloud, and ITOps best practices. Join us.
Thank you for subscribing!




