Last week brought with it a lot of significant updates for the cybersecurity world – some to be cautious about and others worth celebrating.
Let’s start with the good stuff first.
The FBI succeeded in recovering the $2.3 million ransom amount paid to Darkside by Colonel Pipeline.[1] Also, after dominating 2020 as the 4th most prevalent malware, Trickbot remained in the news for its coder getting arrested by the U.S Department of Justice.[2]
Now, let’s move onto the other updates.
Here’re some key highlights more on what all happened in the last week, collated with the help of KNOW, Netenrich’s Threat Intelligence search engine.
Avaddon ransomware shuts shop and gives up decryption keys for free
In an apparent shut down of its operations, Avaddon (a ransomware-as-a-service group) handed over decryption keys for over 2900+ victims to Bleeping Computer.[3] The keys have been identified to be genuine and victims can get back access to their data using a free decryptor tool released by Emisoft.[4] It is not known why it decided to suddenly shut down its operations. However, this could be a result of recent increased scrutiny by law enforcement and governments across the world.
How it started and who are Avaddon ransomware victims?
First identified in 2019, the group gained notoriety for its aggressiveness ever since June 2020. It has been observed to combine encryption with data theft and extortion. Most of the ransomware attacks carried out by its “affiliates” or customers are carried out using phishing and spam campaigns.
The release of 2900+ keys also came in as a surprise wherein earlier only 190 victims were identified. 50% of its victims have less than $10 million annual revenue and belong to various industries including manufacturing, logistics, and the energy sector.
On average, the threat actor demanded around $600k in ransom. Of lately, it exhibited an unusual behavior by accepting the last counteroffer without any further push back. As per LeMagIT, “the diversity of the ransoms paid by the victims of Avaddon, with sometimes very low amounts, suggests that a significant part of the victims paid, but very modest sums: small organizations playing their survival.”
Fancy Lazarus makes a return with a DDoS extortion campaign
After staying out of action for nearly two months, Fancy Lazarus resurfaced again with DDoS attacks. The new chain of attacks suggests its focus against companies with unprotected assets across organizations of all sizes in various industries.
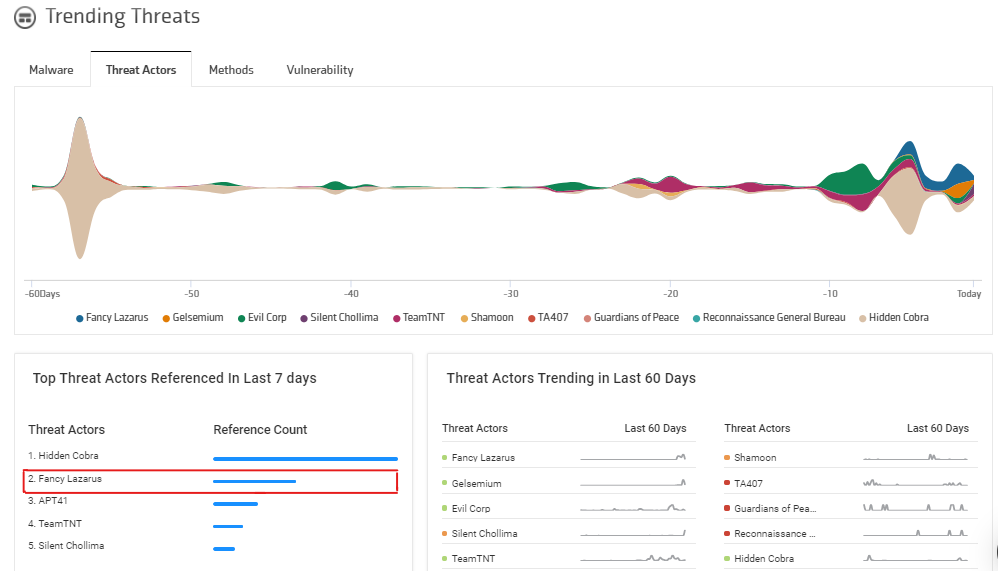
Source: KNOW Threat Intelligence Dashboard
What are the latest updates on Fancy Lazarus?
In the last three weeks, Fancy Lazarus has been sending ransom letters to various Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and Cloud Service Providers (CSPs). In their letters, they give their victims seven days to pay ransom in the form of Bitcoin. The interesting part is this time, they have reduced the ransom demand to 0.5 Bitcoins (USD 19,000 approx.) and 5 Bitcoins (USD 1,98,000 approx.) from earlier 10 to 20 Bitcoins.[5] The ransom increases by double the amount when the deadline is missed and increases by one Bitcoin each day after that.
Currently, the targets are mostly located in the U.S. The ISPs and CSPs they have been attacking, though had DDoS mitigation services, were unprepared for a large-scale globally distributed attack.
Security recommendations:
- Deploy hybrid DDoS protection for on-premise and cloud environments.
- Early threat detection technology that detects and blocks anomalies.
- Real-time resolution to protect from unknown and known threats, including zero-day attacks.
- Updated and a real-time stream of threat intelligence with greater context to protect against known and unknown attackers.
- Draft a security emergency response plan to deal with such scenarios.
Trending common vulnerabilities and exposures: CVE-2021-31955 and CVE-2021-31956
On 8th June, Microsoft released patches for CVE-2021-31955 and CVE-2021-31956. These patches are related to a series of targeted attacks utilizing zero-day exploits in Google Chrome browser and Microsoft Windows devices.[6] The attacks have been carried out by a threat actor named Puzzlemaker.
As per the security analysts, a series of targeted attacks are to be expected now that Microsoft has publicly released the patches.
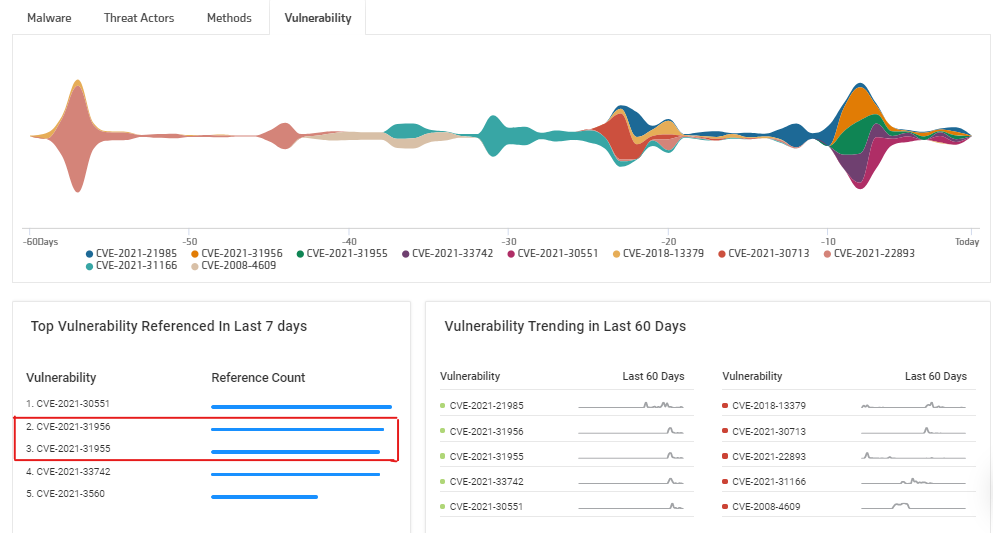
Source: KNOW Threat Intelligence Dashboard
While the first vulnerability CVE-2021-31955 is an Information Disclosure Vulnerability that leaks sensitive kernel information. It is connected to SuperFetch – a feature released in Windows Vista to reduce software loading time by preloading commonly used applications into memory. The second vulnerability CVE-2021-31956 is an Elevation of Privilege vulnerability and is a heap-based buffer overflow.
By combining them, the attackers were able to elevate their privileges and compromise the targeted devices. They were also able to drop a remote shell using which they could upload and download files, create processes, and execute commands such as sleep for a certain time and delete itself from the device.
Security recommendations:
- Update your Chrome and download the latest patches from Microsoft as soon as possible.
- Deploy a reliable endpoint detection and resolution intelligence tool that enable faster detection, investigation, correlation, and remediation. All of this is available with Netenrich.
- Provide your SOC team with real-time and updated threat intelligence.
Keep a track of the latest on all the above and more using Netenrich’s Knowledge Now and get the latest threat intel in your inbox.
Get your free account
Subscribe To Our Newsletter!
The best source of information for Security, Networks, Cloud, and ITOps best practices. Join us.
Thank you for subscribing!




